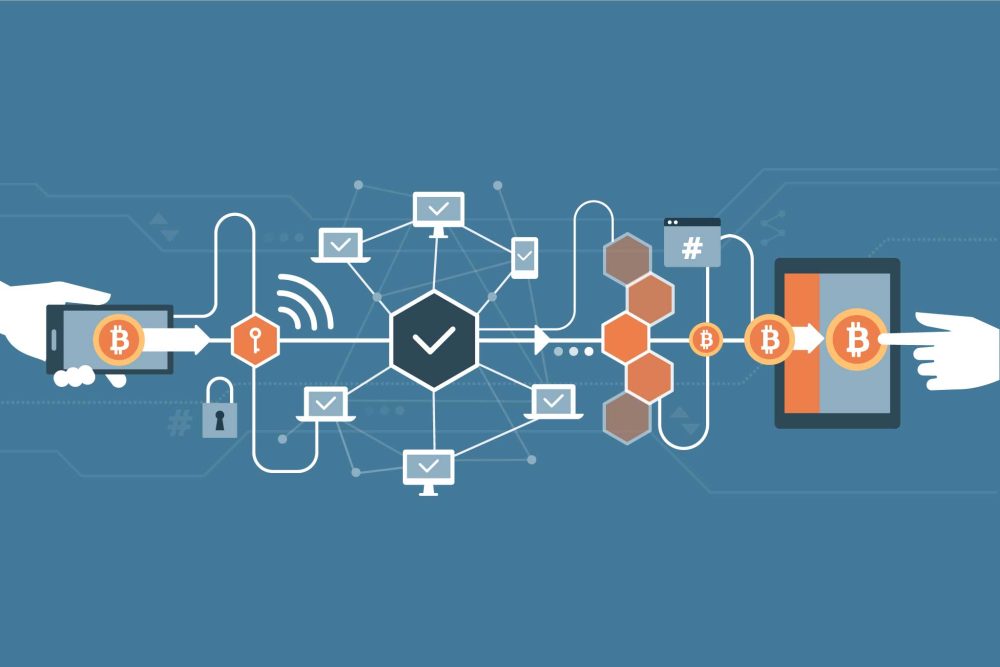
Modern technologies are rapidly changing the economy, finance, logistics, and even government management. One of the key tools of the digital revolution is blockchain platforms. These systems allow creating decentralized, secure, and transparent digital environments that eliminate intermediaries.
Since 2008, when the first Bitcoin block appeared, the technology has become the foundation of new digital solutions. What is a blockchain platform and how does it transform business processes? Let’s find out more in the article.
How Blockchain Platform Works
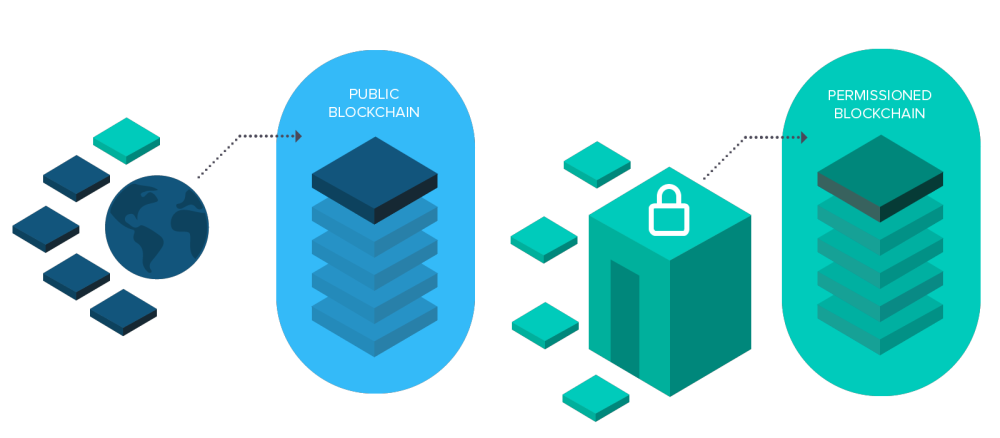
A decentralized platform is a data storage system where information is recorded in a chain of sequential blocks. Each block includes a cryptographic link to the previous one, ensuring protection against tampering. The system operates thanks to consensus algorithms, such as Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake, which confirm the accuracy of the information. What is a blockchain platform from a business perspective? It is a way of storing, transmitting, and processing data without a single central control.
Decentralization: Myth or Necessity
One of the main advantages of blockchain platforms is decentralization. In centralized systems, data is stored on servers under the control of a single company. In blockchain, each transaction is recorded simultaneously by all network participants, eliminating data tampering, reducing the risks of fraud and hacking. Decentralization makes the system resilient to attacks and protects it from manipulation.
However, decentralized solutions have their limitations. The absence of a central governing body complicates decision-making, and transaction processing requires significant computational power. Platforms like Polkadot offer hybrid solutions, combining the strengths of centralized and decentralized networks, improving operation speed and usability.
Applications of Blockchain Platforms
Applications in various fields: financial services, healthcare, logistics, and even government management. In the banking sector, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries in money transfers, reducing fees and speeding up transactions. In healthcare, technologies allow storing patients’ medical records in a secure system accessible only to authorized specialists.
Smart Contracts
One of the key tools used in blockchain platforms. It is a code program that autonomously executes agreement conditions without intermediaries. A smart contract is an algorithm that operates on an “if-then” principle: when certain conditions are met, obligations are automatically fulfilled. In real estate rental, a blockchain contract can facilitate the transfer of a digital key after the deposit payment, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Smart contracts allow automating processes that previously depended on lawyers, banks, or notaries. This is relevant in international settlements, where standard payments can take several days. Using blockchain enables conducting operations within minutes.
Developers choose platforms for creating smart contracts based on their goals. The most popular system is Ethereum, allowing programming complex contract conditions. Hyperledger and Corda also offer specialized business-oriented solutions tailored to corporate needs.
Main advantages of blockchain contracts:
- Elimination of intermediaries and minimization of human error.
- Automatic execution of conditions when events occur.
- High transaction speed compared to traditional methods.
- Increased transparency and immutability of data.
- Potential integration with various digital ecosystems.
Examples of Blockchain Platforms
The smart platform market is rapidly growing, and there are now many solutions adapted to different tasks. Examples of blockchain platforms include both universal networks and specialized systems for corporate use.
Key market players:
- Ethereum — the most popular network for creating smart contracts and decentralized applications.
- Bitcoin — the first and largest cryptocurrency using blockchain as a decentralized transaction ledger.
- Hyperledger — a corporate business solution created under the Linux Foundation.
- Corda — a platform focused on the financial sector.
- Solana — a high-speed network focused on scalability.
- Polkadot — an innovative network allowing the integration of different blockchains into a unified ecosystem.
How to Create Your Own Blockchain
Creating your own blockchain system is a complex process that requires a thoughtful approach to network architecture, consensus algorithms, and security. How to create your own blockchain: the first step is to define the goal and application area of the technology. It is important to understand what type of network is needed: public, private, or consortium.
The choice of consensus algorithm plays a crucial role in network construction.
Among the most popular options:
- Proof-of-Work, providing a high level of security.
- Proof-of-Stake, saving resources.
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake, increasing transaction processing speed.
After choosing the algorithm, it is necessary to develop the network infrastructure. Platforms like Ethereum and Hyperledger are used for this purpose. They allow configuring blockchains for specific tasks. A mechanism of smart contracts is also developed to regulate the network’s internal processes. Smart contract programming is done in languages like Solidity (for Ethereum) and Rust (for Solana).
The next step is testing the system. Load tests should be conducted to determine how resilient the network is to overloads and attacks. After successful testing, the network is launched into operation, where monitoring and optimization of its operation take place.
What Is a Blockchain Platform: Conclusions
Blockchain platforms are the foundation of the new digital economy. They allow building secure, transparent, and automated systems that simplify interactions in business and finance. What is a blockchain platform if not a step towards a decentralized future where each user can control their data?