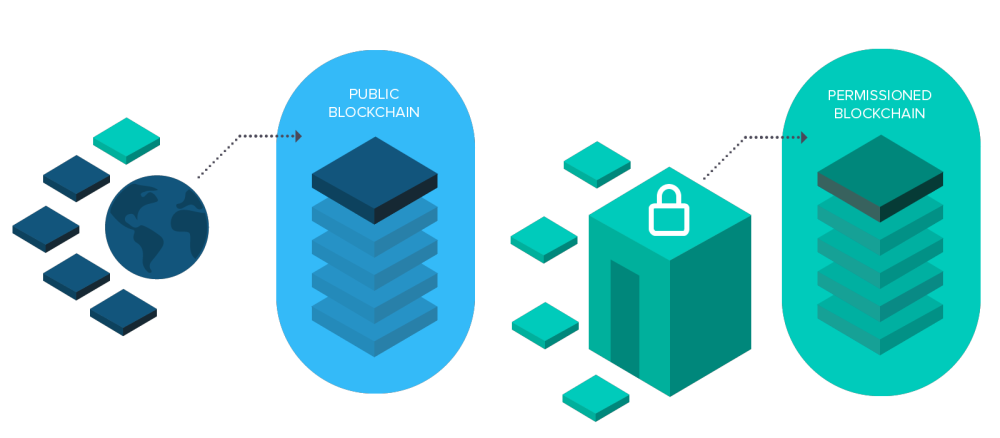
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we store and process information. Its operation is based on a distributed ledger system, where data is recorded in blocks that are linked together in a chain using cryptographic hashes. Each new link contains information about the previous link. This consists of a continuous sequence that cannot be changed or deleted. This makes blockchain technology unique in guaranteeing security and transparency.
How Blockchain Technology Works: Basic Functions and Operations
Blockchain works on the principle of decentralization, which eliminates the need for a central server. All network participants have a copy of the ledger, eliminating the need for a single data management center. All information is encrypted using a special algorithm that generates a unique hash for each block. Any change in this section changes the hash, making it virtually impossible to forge.
For example, the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm is used to record a transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain. In this, miners have to solve complex mathematical problems to confirm transactions. There is also a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm, where the probability of creating a new block depends on the number of coins a participant holds.
These systems guarantee the security and integrity of data, which makes them popular not only in cryptocurrencies, but also in other sectors.
Advantages and disadvantages of blockchain algorithms
 Each algorithm has its advantages and disadvantages. Proof of work offers a high level of security, but requires enormous computing power and consumes a lot of electricity. For example, the Bitcoin network consumes about 110 TWh per year, more than some countries consume.
Each algorithm has its advantages and disadvantages. Proof of work offers a high level of security, but requires enormous computing power and consumes a lot of electricity. For example, the Bitcoin network consumes about 110 TWh per year, more than some countries consume.
Unlike PoW, Proof-of-Stake is more efficient and faster, but less secure against potential attacks. This has certain disadvantages when used in heavily loaded networks. Nevertheless, the characteristics of blockchain technology make it possible to tailor algorithms to specific tasks, striking a balance between speed, security and cost.
Advantages of Blockchain: What makes it unique?
Blockchain technology stands out due to its unique advantages over traditional databases. The most important ones are transparency, decentralization and security.
Technology that creates trust
Every network participant can trace the transaction history from the first link. In the banking sector, this helps combat fraud and increase customer trust. For example, blockchain-based systems are used to verify payments and process smart contracts.
Security is ensured by cryptography and distributed data storage. It is impossible to change the information in a section without changing the entire text. Piracy is therefore virtually impossible.
Advantages for participants in the process
The system eliminates intermediaries, which reduces costs and streamlines data processing. It allows the movement of goods in supply chains to be monitored in real time and minimizes the risks of loss and counterfeiting in logistics.
Blockchain also increases the scalability of networks. For example, new solutions such as the Lightning Network make it possible to process thousands of micropayments per second, thus reducing the load on the main network.
Disadvantages of blockchain: the other side of the coin
Despite its many advantages, the specific characteristics of blockchain technology entail certain limitations and create difficulties in its implementation.
Why is Blockchain often criticized?
One of the biggest problems is the high energy costs. Proof-of-work technology requires a huge mining power. For example, mining one Bitcoin transaction requires as much energy as the average American household consumes per month.
Scalability issues also limit the use of blockchain in high-load systems. For example, the Ethereum network can only process about 15 transactions per second, which is not suitable for large payment systems.
Risks of using data in the blockchain
Despite its decentralization, the blockchain is not protected against errors by network participants. If a user loses access to his or her wallet, it is impossible to recover the data. In addition, the lack of uniform standards makes it difficult to integrate blockchain into existing data management systems.
Blockchain applications: from cryptocurrencies to the public sector
The characteristics of blockchain technology allow it to be applied not only in the financial sector, but also in healthcare, logistics, and even in public administration:
- Blockchain application in Russia. The method is currently being actively implemented in the country to create transparent voting systems, manage land registers, and streamline the flow of documents. In 2020, Moscow Exchange launched a blockchain platform for accounting digital assets. A comparison with foreign experiences shows that Russia is moving with the times and adapting blockchain technology to national characteristics and legislation.
- Blockchain and cryptocurrencies: inextricably linked. The emergence of Bitcoin in 2009 was the first successful application of the method. Since then, this technology has formed the basis of thousands of cryptocurrencies. Each currency transaction on the network is recorded in blocks, ensuring transparency and security.
- The future of blockchain in various sectors. The system has the potential to transform medicine, logistics and education. In healthcare, blockchain technology makes it possible to store and transmit medical data without the possibility of manipulation. In logistics, it simplifies product tracking and process automation.
Conclusion
 The possibilities of blockchain technology offer new opportunities for companies and governments. The advantages of security, transparency and decentralization make the system an important method of the future. Despite the existing shortcomings, blockchain continues to develop and adapt to the needs of modern times.
The possibilities of blockchain technology offer new opportunities for companies and governments. The advantages of security, transparency and decentralization make the system an important method of the future. Despite the existing shortcomings, blockchain continues to develop and adapt to the needs of modern times.
 en
en  de
de  ar
ar  es
es  nl
nl  hi
hi  fr
fr  it
it  pt
pt  el
el