The world of digital technology has exploded thanks to blockchain, a powerful and multifunctional system that is not only changing the way we think about financial transactions but is also reshaping almost every industry. The essence of blockchain is not just a series of blocks and data, but a radically new form of information storage and transfer that eliminates intermediaries, reduces the risk of fraud, and makes processes transparent. This technology has already attracted the attention of major companies and governments, including the Russian Federation.
What Blockchain is and how it works
A digital ledger in which information is recorded in successive, interconnected blocks. The essence of blockchain: imagine an invisible chain of data where each block is protected by a complex cryptographic code – a hash. The hash is created to protect the information. If someone tries to change the data in one block, it affects all subsequent blocks. Blockchain technology is based on transparency and reliability: once the data is written down, it cannot be changed.
After forming the basis for Bitcoin, blockchain has developed into a standalone technology that goes far beyond cryptocurrencies. The essence of this is that trust between the participants in the process is not mediated by a third party (for example, a bank), but by an algorithm. That’s right, decentralization bypasses many problems associated with the human factor.
What is the essence, and why is blockchain needed?
Technology has replaced old centralized systems that were vulnerable to corruption, malfunctions and hacking. Thanks to blockchain, it is possible to guarantee the transparency and reliability of transactions. For example, in Russia, the technology is used to track supply chains, make them more efficient and prevent counterfeiting.
One of the best examples is its use in government systems. The Russian Federation is already experimenting with its application in the electoral system, which helps prevent fraud and ensures the integrity of elections.
Blockchain principles: Why is decentralization important?
Decentralization is the cornerstone of blockchain’s operation. Imagine a system in which there is no central authority that can control or change data. The information is stored on thousands of computers (nodes), and each participant has the same rights. If one computer fails or is hacked, the others will continue to work and ensure the integrity of the data.
The goal of decentralization is to make the blockchain system resistant to attacks and errors because there is no single point of failure. This is especially important for financial and government systems, where failure or fraud can have serious consequences.
An example of a decentralized system using blockchain
One of the clearest examples of decentralized systems is the Ethereum platform, which has taken the concept to a new level. Ethereum has been used to develop thousands of smart contracts: automated agreements that are executed without human intervention. This allows companies to automate their processes and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
Another important example is decentralized applications (dApps) that run on the blockchain. They are used in a variety of sectors, from gaming to finance, and offer a high degree of transparency and security. Russia has also started developing similar solutions, for example, for logistics and accounting of state assets.
Blockchain Structure: What’s Behind This Technology?
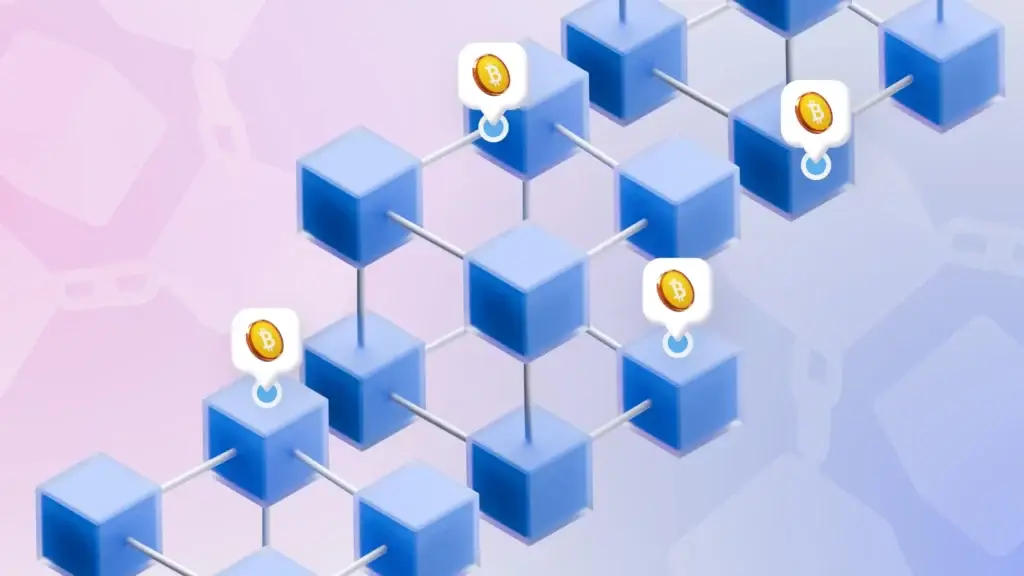 The structure consists of many elements that work together to form a system that is protected from outside influences. Each block contains three main components: data, a hash of the current block, and a hash of the previous block. These hashes are unique cryptographic keys that link the blocks together and ensure the security of the chain.
The structure consists of many elements that work together to form a system that is protected from outside influences. Each block contains three main components: data, a hash of the current block, and a hash of the previous block. These hashes are unique cryptographic keys that link the blocks together and ensure the security of the chain.
A blockchain starts with a so-called genesis block – the first block in the chain. Each new block is then added through the mining process, which involves performing complex cryptographic tasks. This technology ensures that a new block is only added after the network has confirmed it. The result is a secure, unbroken chain of data that cannot be changed or deleted.
The importance of nodes
The nodes in the blockchain are the computers that keep the entire system running by storing information about all transactions and validating them. They act as independent guardians of the data and participants in the network: they are not subordinate to a central server, but act as part of a decentralized system.
Each node owns a complete copy of the blockchain and is responsible for verifying new blocks. If the data in a block does not comply with the rules of the network, it is rejected by the nodes. This makes the system transparent and reliable, because the data is verified by multiple participants.
Applications and perspectives of blockchain: advantages and disadvantages
The advantages are clear. First of all, there is transparency: all data is accessible to all participants in the network, which eliminates fraud. In addition, the blockchain offers security: the data is protected by cryptography and cannot be changed. Another advantage is the absence of intermediaries. This allows companies to save on transactions and simplify processes.
But there are also disadvantages. One of the biggest problems is the high energy consumption during mining. To keep the blockchain running, a lot of computing power is needed, which entails high energy costs. There is also a problem with scalability: as the network grows, the load on the nodes increases, which can slow down the system.
Examples of blockchain use in Russia
In Russia, the technology is actively used in various areas. A clear example is the introduction of blockchain to trace the origin of goods. Large companies such as Nornickel use them to manage their supply chains and ensure transparency of their activities.
This technology is also being used in the public sector. Moscow has already started pilot projects based on blockchain technology for the management of state assets and the registration of real estate rights. This makes the processes more transparent and prevents corrupt practices.
The future of blockchain and cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether have already proven themselves as decentralized means of payment. The future of blockchain lies in the development of smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi), which allow users to manage their finances without banks.
In the field of quantum blockchain, there are also developments that will offer even higher levels of security and performance. Scalability and energy costs are being considered.
Conclusion
 The core of blockchain is decentralization and transparency. This makes it a revolutionary technology for many sectors. The future of this technology lies in innovation, which will only accelerate its adoption.
The core of blockchain is decentralization and transparency. This makes it a revolutionary technology for many sectors. The future of this technology lies in innovation, which will only accelerate its adoption.
 en
en  de
de  ar
ar  es
es  nl
nl  hi
hi  fr
fr  it
it  pt
pt  el
el 









